In the Internet world, there’s nothing worse than sitting around, waiting for a website to load.
For businesses, a few extra seconds may be the difference between a sale and a customer forever lost.
It may not seem like much, but just about every fraction of a second it takes your website to load, more and more customers backtrack and return to the search engine in order to seek out a faster website. This is true even if you have a better product and offer higher-rated services than the company.
Thankfully, it isn’t all that difficult boosting load time and slashing seconds from a potential customer’s wait time.
While what’s causing your load time to drag may differ from the next company website, chances are if you take advantage of these seven principles, you’ll not only see a boost in website speed you’ll also see improvements in just about every other important bit of website analytical data, including sales and search engine ranking.
You can also watch this video to get a better understanding of improving site speed.
1) Cut HTTP Requests
At the beginning of every website is the HTTP (or HTTPS). Short for hypertext transfer protocol, it represents the transfer of information from a website to the accessing browser. The more HTTP requests a website has the longer it takes for the site to load. This is because the data requests don’t all transfer instantly. It transfers one at a time, so every additional HTTP request extends the load requirement.
What exactly is an HTTP request? Every image, every block of text, every uploaded video, and every style sheet represents an individual HTTP request. So every additional one of these requests increases your website load time. For an HTTPS the visually complete time is even longer.
This means the fewer HTTP or HTTPS requests a website has the less information it needs to bounce in between a server and an Internet browser. The fewer bounces the faster the website loads, which cuts down on the site’s bounce rate.
(Source)
According to KeyCDN (2017), HTTPS performance does take longer to visually complete loading a website, yet offering this added level of security is critical. Not using HTTPS now hinders your search engine ranking, so a website designer needs to take into account not only website security but the number of requests permitted as well.
2) Time To First Byte
Referenced as TTFB, this is the amount of time it takes to begin downloading the data from a website’s host server. As references in the graph above, HTTPS websites have a slightly longer wait time until time to the first byte as opposed to standard HTTP.
The faster a website’s TTFB the faster information begins to load. When content loads faster a website user is less likely to back out right away. Essentially it buys the rest of the website some time to load. When a website lingers on a white screen for extended periods of time this is a display of a longer than normal TTFB.
The amount of coding information going on in the background influences the TTFB. A streamlined build of a website cuts down much of the loading fog, allowing it to run smoothly and effortlessly.
In order to make this upgrade, a website would need to transfer to a different website platform, which would more or less result in a complete redesign of the site. For some websites, this may not be possible but for others looking to build a new site or construct a company site for the first time, knowing which website platform offers the fastest TTFB is beneficial.
According to Pantheon (2018), the average WordPress website has a TTFB of nearly 1200 milliseconds (MS) or 1.2 seconds. The average website, regardless of platform, has a TTFB of 750, while platforms using Pantheon are around 350 milliseconds. This illustrates the importance of researching the right website platform to use before signing up as it does play a role in load time.
(Source)
3) Allow Caching
When an individual returns to a website it generally loads faster. This is because caching is activated. The information the user’s computer downloaded remains stored in a folder on the computer, so the next time they visit the site the information is already present. When setting up the website it is important to select this caching feature. While it doesn’t help with the initial load time, it does help with subsequent load times.
Often a visitor will not make a purchase on their first visit but instead on a secondary visit. This is where the cached information comes in handy. According to Crazy Egg (2018), the optimal load time for a heightened conversion rate is 1.65 seconds (or 1650 milliseconds). This load time has a 2.9 percent conversion rate. A website with a load time of just a second longer experiences a conversion rate drop to nearly 1.5 percent, slashing it in half.
(Source)
4) Format Your Images For the Internet
After an Internet browser and a Website host have interacted with regards to HTTP requests the browser begins to download information. While the number of HTTP requests slows down the initial download time and the TTFP, the file size of images on the website drags out the download process. Due to this, it is important to format images for the Internet.
When capturing an image from a cell phone or camera, the original picture is usually at least a few megabytes worth of data if not larger. By formatting the image down to an appropriate Web format, it shaves dozens of megabytes off the load time. As the graph below from The Goodies Life points out, the optimal image size for full image visibility is 1400 x 900 (89 percent of visitors will be able to see the image without any compression or needing to resize the image on their device).
(Source)
Additionally, the image can be further compressed down in a photo-editing program where the quality is reduced. This cuts down on the file size, shaving away valuable megabytes, which allows for a faster website download time.
(Source)
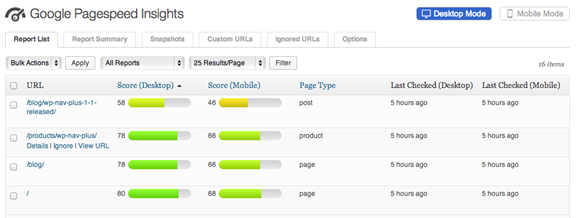
5) Google Pagespeed Insights
Google provides a number of helpful tools and features for website creators to take advantage of. This includes Google Pagespeed Insights, which provides businesses and website creators with all the information they need to monitor website performance in terms of speed. It splits insights into load times for not just desktops and mobile, but different operating systems as well.
Google Pagespeed Insights, as WordPress points out, allows users to monitor performance after updating the site, adding in new HTTP requests and to see how the site fairs on a given host server. This way, if a company is considering a site transfer to a different host they can see how the site performs.
(Source)
6) Website Redirects
Redirects send visitors on a website to a different page or different area of the site. Every redirect a website has is seen as a new HTTP request. As HTTP requests are weighed the same a website with one image and five redirects will have the same HTTP requests as a website with five images and one redirect. In order to help boost the speed of a website’s load time, it is important to identify unnecessary website redirects and remove these from the site.
As SEO PowerSuite points out, a collection of non-essential redirects has the potential of dragging down website performance. In the example below the website has six unnecessary redirects which extend load time by nearly a full second. This individual second delay may cut converted leads in half.
(Source)
There are a number of tools available to reduce the number of unnecessary redirects from a website. Google Analytics provides information on a website’s links while other services like Screaming Frog SEO, Google Search Console, and other similar programs provide an ability to scan over a website and identify these non-essential redirects.
7) Go Over Hosting Options
A website’s host is more than just a server housing the website’s data and stored information. It plays a pivotal role in download speed. There are three options available when it comes to this, including a dedicated server, shared hosting and VPS hosting.
VPS hosting with a dedicated server provides faster download speeds as each individual who visits the website connects through individualized server resources. This way, the user does not compete with others visiting the site. This kind of hosting method is more expensive but beneficial for website experiencing more traffic.
A shared hosting option using a dedicated server though is less expensive, but it will slow down Internet traffic for more popular sites as multiple Internet users are forced to go through the same server resources. At busy times of the day, this can create a bottleneck and slow down website access for all visitors.
(Source)
In Conclusion
Website speed is more important than you might initially believe. What may just be the difference of one or two seconds is often the difference between a sale, a new lead, and a higher search engine ranking. All of this is available to you, simply by taking advantage of these seven principles and making a few slight adjustments to your website. With a faster website, you’ll experience heightened site analytics across the board, so there’s no better time than the present to implement these slight alterations.